NHS Wales – SNOMED Maturity Levels for Health Care systems
Level
Definition
Example(s)
1
No use of SNOMED CT.
1. A clinical cardiology system that records diagnosis as free text.
2. A clinical system that uses its own codes for recording a patient’s current medical conditions e.g.
1 = Heart Attack,
2 = Asthma,
3 = Stroke,
4a = Diabetes type1,
4b = Diabetes type2,
2
Uses SNOMED externally to generate lists that are then used for creating its internal coding schemes.
A clinical system that has structured data entry at the user interface of certain clinically relevant data items uses SNOMED to generate lists that are either hard-coded into the system user interface drop-downs or used to create reference data tables in the system.
These ‘lists’ are usually created by doing a manual search and curation of SNOMED content – typically using a SNOMED browser or published spreadsheets of SNOMED content.
The system holds these descriptions but does not hold any SNOMED codes.
This example uses descriptions copied from SNOMED:
1 = Myocardial infarction,
2 = Asthmatic,
3 = Ischemic stroke,
4a = Diabetes mellitus type 1,
4b = Diabetes mellitus type 2,
3
Imports SNOMED concepts and/or descriptions into its reference database as a flat list.
Uses SNOMED reference data alongside other coding schemes in its own internal reference database.
A system has its own set of internal reference tables.
In some cases, these can be populated directly from the SNOMED release files or can be generated manually from using a SNOMED browser.
The system holds both the SNOMED code and its description.
This example uses descriptions and codes copied from SNOMED:
1 = 22298006 = Myocardial infarction
2 = 195967001 = Asthmatic,
3 = 422504002 = Ischemic stroke,
4a = 46635009 = Diabetes mellitus type 1,
4b = 44054006 = Diabetes mellitus type 2,
4
Imports SNOMED Concepts and Descriptions and Relationships into its internal reference database.
Systems utilise these SNOMED structures to allow users to navigate, select, store and report on clinical data without hierarchy context.
It stores SNOMED codes and descriptions.
Does not use subsets/refsets or cross maps.
This example shows how synonyms or more detail could be used:
22298006 = Myocardial infarction
Synonyms:
Myocardial
infarction
Infarction of
heart
Cardiac
infarction
Heart
attack
Myocardial infarction
(disorder)
MI - Myocardial
infarction
Myocardial infarct
More detail (children):
Acute myocardial infarction (disorder)
First myocardial infarction (disorder)
Microinfarct of heart (disorder)
Mixed myocardial ischemia and infarction (disorder)
Myocardial infarction in recovery phase (disorder)
Myocardial infarction with complication (disorder)
Non-Q wave myocardial infarction (disorder)
Old myocardial infarction (disorder)
Postoperative myocardial infarction (disorder)
Silent myocardial infarction (disorder)
Subsequent myocardial infarction (disorder)
True posterior myocardial infarction (disorder)
Different hierarchy (finding):
ECG: myocardial
infarction
Electrocardiogram finding of
infarction
Electrocardiographic myocardial infarction
(finding)
Electrocardiographic myocardial infarction
EKG: myocardial
infarction
5
Imports SNOMED Concepts, Descriptions, Relationships, Subsets, and X maps.
The application record architecture has been validated against the SNOMED model to use hierarchy context.
Systems use the SNOMED model to search, validate, select, record and report on clinical information using SNOMED terms.
Imports SNOMED and maps to its own internal reference structures.
Systems utilise these SNOMED structures to allow users to navigate, select, store and report on clinical data without hierarchy context.
It stores SNOMED codes and descriptions.
Can use subsets/refsets or cross maps.
This example shows how refsets or hierarchy could be used:
Hierarchy constrained:
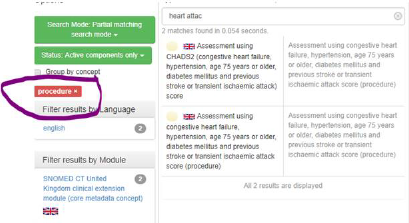
Refset constrained:
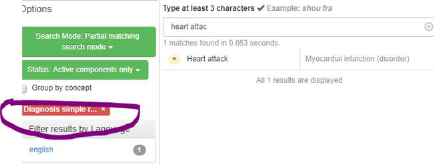
6
Imports and relies on SNOMED Concepts, Descriptions, Relationships, Subsets, and X maps.
The application record architecture has been validated against the SNOMED model.
It uses the SNOMED model to search, validate, select and record clinical information using SNOMED terms.
It uses SNOMED as its base/master reference terminology.
It uses SNOMED concepts wherever appropriate as its reference data lists.
It can handle and relies on SNOMED mapping to multiple different terminologies/coding schemes.
It cannot handle / does not use post coordinated expressions.
7
Imports and relies on SNOMED Concepts, Descriptions, Relationships, Subsets, X maps and uses Post Coordination.
The application record architecture has been validated against the SNOMED model.
It uses the SNOMED model to search, validate, select and record clinical information using SNOMED terms.
It uses SNOMED as its base/master reference terminology.
It uses SNOMED concepts wherever appropriate as its reference data lists.
It can handle and relies on SNOMED mapping to multiple different terminologies/coding schemes.
It can produce, store and interpret post coordinated expressions.
Example of a post coordinated expression:
=== 57809008 |Myocardial disease (disorder)| + 414545008 |Ischemic heart disease (disorder)| + 251061000 |Myocardial necrosis (finding)| + 609410002 |Necrosis of anatomical site (disorder)| : { 116676008 |Associated morphology (attribute)| = 55641003 |Infarct (morphologic abnormality)|, 363698007 |Finding site (attribute)| = 74281007 |Myocardium structure (body structure)| }